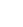
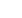
In the dynamic and evolving world of aquaculture, the need for efficient and reliable aeration systems has never been more critical. One standout solution that has garnered significant attention is the float type aerator. These devices play a pivotal role in maintaining optimal water quality and ensuring the health and growth of aquatic species.
A float type aerator is an innovative piece of equipment designed to enhance oxygen levels in water bodies. Unlike traditional aeration methods, float type aerators are strategically placed on the water surface, allowing them to efficiently transfer oxygen into the water column. This is particularly important in aquaculture ponds, where oxygen depletion can lead to significant losses in fish populations.
The primary function of a float type aerator is to increase the dissolved oxygen (DO) levels in water. Oxygen is essential for the respiration of fish and other aquatic organisms. In environments with low DO levels, fish may experience stress, reduced growth rates, and even mortality. By introducing oxygen-rich air into the water, float type aerators create a more conducive environment for aquatic life.
One of the key advantages of float type aer isators their ability to mix water effectively. In ponds, stratification can occur, leading to layers of water with varying temperatures and oxygen levels. This can create dead zones where oxygen is scarce, posing a threat to fish health. Float type aerators break up these layers, ensuring uniform oxygen distribution throughout the pond. This not only improves water quality but also enhances the overall productivity of the aquaculture system.
The design of float type aerators also contributes to their efficiency. Typically, these devices consist of a floating platform equipped with a motor and impeller. The impeller in draws air and water, creating a fine mist that disperses oxygen into the water. This mechanism ensures that a large surface area of water is exposed to air, maximizing oxygen transfer. Additionally, the floating nature of the aerator allows it to move with the water surface, maintaining optimal performance even in fluctuating water levels.
Maintenance is another aspect where float type aerators excel. Their design makes them relatively easy to service and clean. Unlike submerged aerators, which can be difficult to access and maintain, float type aerators can be easily removed from the water for routine inspections and repairs. This reduces downtime and ensures that the aeration system is always functioning at peak efficiency.
In addition to their practical benefits, float type aerators also offer economic advantages. They are generally more energy-efficient compared to other aeration methods, resulting in lower operational costs. This is particularly important for large-scale aquaculture operations where energy consumption can be a significant expense. By reducing energy usage, float type aerators contribute to a more sustainable and cost-effective aquaculture practice.
Moreover, float type aerators can be customized to meet the specific needs of different aquaculture systems. They come in various sizes and configurations, allowing farmers to choose the most suitable option for their ponds. Whether it is a small-scale fish farm or a large commercial operation, there is a float type aerator that can meet the unique requirements of each setup.
The environmental impact of float type aerators is also worth noting. By improving water quality and reducing the need for chemical treatments, these devices contribute to a healthier aquatic ecosystem. This is particularly important in the context of sustainable aquaculture, where minimizing environmental footprint is a key priority.
Float type aerators represent a significant advancement in aquaculture technology. Their ability to enhance oxygen levels, mix water effectively, and maintain ease of maintenance makes them an invaluable tool for modern fish farmers. As the demand for sustainable and efficient aquaculture practices continues to grow, the role of float type aerators in ensuring the health and productivity of aquatic systems cannot be overstated.



 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 عربى
عربى