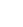
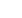
A surge wave aerator is a water aeration device designed to improve oxygen levels in ponds, tanks, and other aquatic systems by using specialized structural designs.
At the core of its operation is the wave-style or jet-propulsion mechanism. Unlike traditional aerators that rely on surface paddles to stir water, surge wave systems produce directed flows that create waves across the water surface. These waves promote efficient oxygen transfer from air to water and help circulate water throughout the pond or tank.
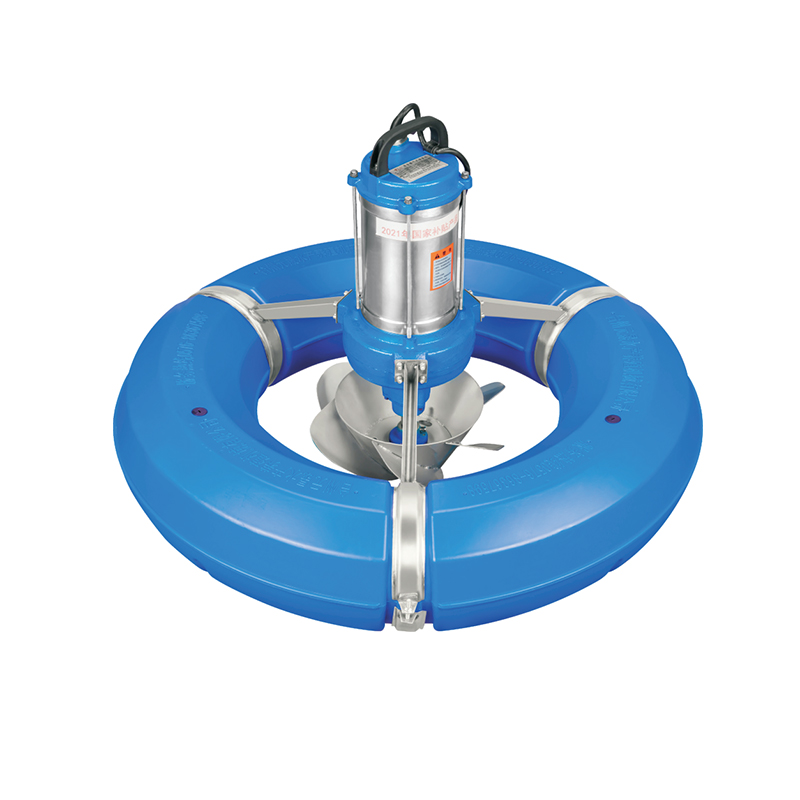

Another significant feature is the helical impeller paired with floating ball structures. The helical impeller, shaped in a spiral form, generates smooth, continuous water movement that supports effective wave generation. The floating balls allow the impeller to adjust automatically to changes in water level, maintaining optimal contact with the water surface. This floating arrangement enhances efficiency without requiring frequent manual adjustment and ensures stable performance even as water levels fluctuate.
Durable materials are an essential aspect of surge wave aerator design. 304 stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant metals are used for housings and fasteners, offering long-term resistance to salt, alkaline water, or organic buildup. HDPE (high-density polyethylene) floats provide reliable buoyancy while resisting chemical degradation, UV exposure, and mechanical impact. These choices allow the aerator to operate effectively in environments such as fish ponds, shrimp pools, and natural water bodies that may experience varying water quality conditions.
The design also emphasizes ease of installation and maintenance. Modular components can be replaced or serviced without specialized tools, reducing downtime and supporting continuous operation. The system can be scaled to suit different pond sizes without sacrificing performance.
Surge wave aerators are commonly applied in fish ponds, shrimp farms, aquaculture tanks, and ecological water bodies, especially during periods of high oxygen demand, such as warm seasons or nighttime hours. During these times, dissolved oxygen levels can decrease due to temperature effects or high biological activity. By increasing aeration, these devices help reduce stress on aquatic organisms and support healthier growth while maintaining water quality.
While these aerators are often electrically powered, they can also be integrated with solar energy systems for off-grid locations. Solar integration provides an alternative energy source, ensuring continuous aeration in remote water bodies without access to the electrical grid.
Overall, the surge wave aerator combines efficient water propulsion, floating adaptive mechanisms, corrosion-resistant materials, and practical structural design. Its features allow for consistent oxygenation, reduced water stagnation, and improved conditions for aquatic life, making it a useful solution for managing ponds and ecological water systems effectively.
FAQ: Surge Wave Aerator
Q1: What is a surge wave aerator?
A surge wave aerator is a device used to improve dissolved oxygen levels in ponds, tanks, and other water bodies. It uses specialized structures to generate waves and circulate water efficiently.
Q2: How does the wave or jet-propulsion structure work?
The wave or jet-propulsion structure creates directed flows and surface waves that enhance oxygen transfer. These waves also help circulate water across the pond, reducing stagnant zones.
Q3: What is the role of the helical impeller and floating balls?
The helical impeller produces smooth, continuous water movement, generating effective waves. Floating balls allow the impeller to adjust to water level changes, maintaining optimal performance automatically.
Q4: What materials are used in surge wave aerators?
Durable materials such as 304 stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant metals are used for structural components, while HDPE floats provide buoyancy and resist chemical or UV damage.
Q5: Where are surge wave aerators commonly used?
They are commonly used in fish ponds, shrimp farms, aquaculture tanks, and ecological water bodies, especially when dissolved oxygen levels may be low due to temperature or biological activity.


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 عربى
عربى